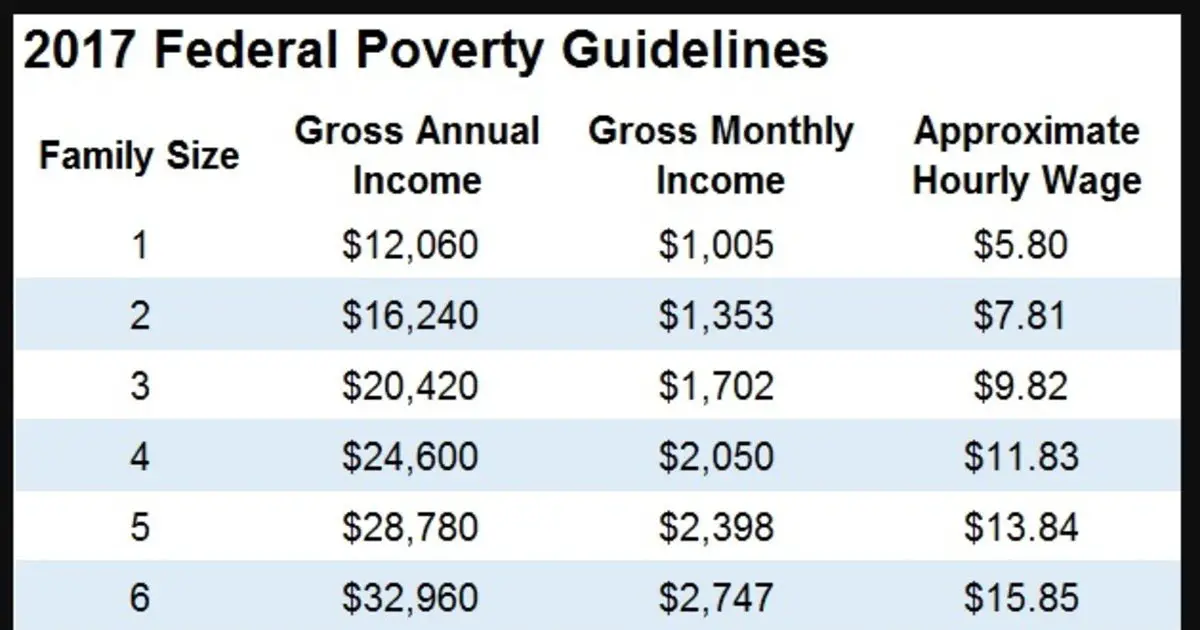
What Is A Nerve Agent
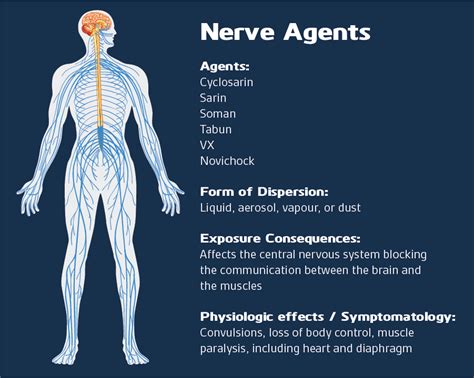
Nerve agents are a class of highly toxic chemical compounds that act on the nervous system, disrupting the body's ability to transmit nerve impulses and leading to severe physiological effects. These agents, often synthetic in nature, have been developed and utilized for their potent and rapid impact on human physiology, making them a significant concern in the realm of chemical warfare.
Understanding Nerve Agents
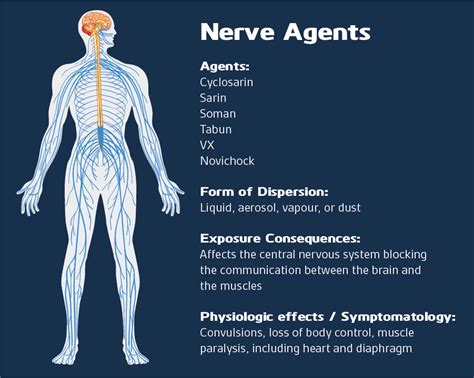
Nerve agents are organophosphorus compounds, similar in structure to certain pesticides, but far more potent. They operate by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which is responsible for breaking down acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter crucial for muscle function and other vital processes. When this enzyme is inhibited, acetylcholine accumulates in the body, leading to overstimulation of muscles and other organs.
The effects of nerve agents can be devastating and rapid. Exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or absorption through the skin. Symptoms include a runny nose, tightness in the chest, eye pain, drooling, muscle twitching, seizures, and ultimately, death if not treated immediately.
Common Nerve Agents

There are several well-known nerve agents, each with its own unique properties and effects:
- Tabun (GA): One of the earliest nerve agents developed, Tabun is a clear, colorless, and highly volatile liquid with a faint fruity odor. It is highly toxic and can cause severe symptoms even in small doses.
- Sarin (GB): A more potent nerve agent than Tabun, Sarin is a clear, colorless, and highly volatile liquid with a slight odor of rotten fruits. It is rapidly absorbed through the skin and can cause symptoms within seconds of exposure.
- Soman (GD): Similar to Sarin but more potent and persistent, Soman is a clear, colorless liquid with a slight camphor-like odor. It is known for its ability to penetrate clothing and skin, making it a particularly dangerous agent.
- VX: The most toxic of all known nerve agents, VX is a thick, amber-colored liquid with virtually no odor. It is extremely persistent in the environment and can remain active on surfaces for extended periods.
The Impact of Nerve Agents

The impact of nerve agents on human health is profound and often irreversible. Exposure can lead to long-term neurological damage, respiratory failure, and death. The effects are not limited to humans; these agents can also harm animals and damage the environment, making them a significant threat to public health and safety.
Protection and Treatment

Protecting against nerve agent exposure involves the use of specialized equipment, such as gas masks and protective suits. Decontamination procedures are also crucial to removing any traces of the agent from the body or environment. Treatment for nerve agent exposure typically involves the administration of atropine and pralidoxime chloride (2-PAM), which can help reverse the effects of the agent and provide temporary relief.
Regulations and Control

Due to their extreme toxicity and potential for misuse, nerve agents are strictly regulated by international treaties, such as the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC). The CWC prohibits the development, production, stockpiling, and use of chemical weapons, including nerve agents. However, despite these regulations, illicit production and use of nerve agents continue to pose a significant threat to global security.
Conclusion
Nerve agents are a serious threat to global security and public health. Their development and use have been a significant concern in the realm of chemical warfare, and their impact on human health and the environment cannot be overstated. Understanding the properties and effects of these agents is crucial for developing effective protection, treatment, and regulatory measures.
What are the symptoms of nerve agent exposure?

+
Symptoms of nerve agent exposure can include a runny nose, tightness in the chest, eye pain, drooling, muscle twitching, seizures, and in severe cases, respiratory failure and death.
How can I protect myself from nerve agents?

+
Protection against nerve agents involves the use of specialized equipment, such as gas masks and protective suits. It’s also important to follow decontamination procedures if exposure is suspected.
What is the treatment for nerve agent exposure?
+
Treatment typically involves the administration of atropine and pralidoxime chloride (2-PAM) to reverse the effects of the nerve agent and provide temporary relief.
Are nerve agents still used in warfare today?

+
While the use of nerve agents is prohibited by international treaties, there have been instances of their use in recent conflicts, highlighting the ongoing threat they pose to global security.