Trunk Of A Body

The human body is a complex and fascinating structure, composed of various interconnected systems and components. Among these, the trunk, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall balance, stability, and mobility. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the trunk, exploring its anatomical structure, functions, and the impact it has on our daily lives.
Understanding the Trunk

The trunk, also known as the torso or the core, is the central part of the human body, extending from the neck to the pelvis. It serves as a vital link between the upper and lower body, providing a stable base for movement and supporting the weight of the head, arms, and legs. Comprising a complex network of bones, muscles, ligaments, and organs, the trunk is a powerhouse that enables us to perform a wide range of physical activities.
Anatomical Composition
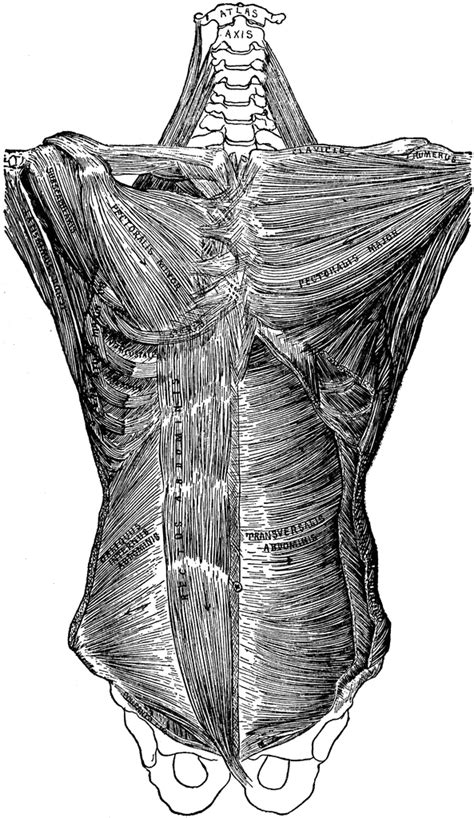
The trunk is primarily made up of the axial skeleton, which includes the skull, spine, and rib cage. These structures provide protection for vital organs and serve as attachment points for various muscles.
Bones and Vertebrae
The spine, or vertebral column, is a crucial component of the trunk. It consists of 33 individual bones called vertebrae, which are stacked on top of each other and connected by discs. These discs act as shock absorbers, allowing the spine to bend and twist while maintaining stability.
The vertebrae are divided into five regions: cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), lumbar (lower back), sacrum, and coccyx (tailbone). Each region has a specific function and range of motion, contributing to the overall flexibility and strength of the trunk.
Rib Cage and Sternum
Encircling the chest, the rib cage, or thoracic cage, is a protective bony structure that houses vital organs such as the heart and lungs. It consists of 12 pairs of ribs, which are connected to the spine at the back and the sternum (breastbone) at the front. The rib cage provides structural support and protects the internal organs from external impact.
Muscles and Connective Tissues

The trunk is home to a vast array of muscles, each with its own unique function. These muscles can be broadly categorized into three groups: abdominal muscles, back muscles, and oblique muscles.
- Abdominal Muscles: These muscles, including the rectus abdominis, internal and external obliques, and transversus abdominis, are responsible for flexing the trunk, stabilizing the spine, and maintaining posture. They also play a crucial role in respiratory function.
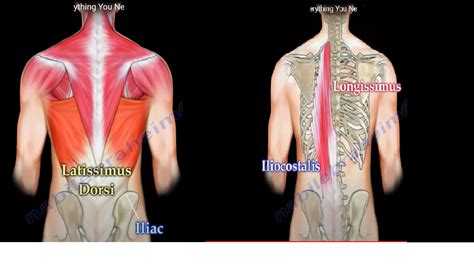
- Back Muscles: The back muscles, such as the erector spinae and the latissimus dorsi, provide support and stability to the spine. They enable us to extend, rotate, and bend our trunk, allowing for a wide range of movements.
- Oblique Muscles: Located on the sides of the trunk, the oblique muscles help with lateral flexion and rotation. They assist in maintaining balance and stability during various activities.
In addition to muscles, the trunk also contains a network of ligaments and connective tissues that provide structural support and stability. These include the intervertebral ligaments, which connect the vertebrae, and the costovertebral ligaments, which attach the ribs to the spine.
Functions of the Trunk

The trunk serves multiple essential functions that contribute to our overall well-being and physical capabilities.
Support and Stability

One of the primary functions of the trunk is to provide support and stability to the entire body. The complex interplay of bones, muscles, and ligaments allows us to maintain an upright posture, balance our weight, and perform various activities without falling or losing balance.
Movement and Mobility

The trunk acts as a central hub for movement. The flexibility and strength of the spine, combined with the powerful muscles of the trunk, enable us to perform a wide range of motions, including bending, twisting, and reaching. These movements are essential for everyday tasks, sports, and recreational activities.
Protection of Vital Organs

The rib cage and spine play a crucial role in protecting vital organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys. The sturdy structure of the trunk acts as a shield, safeguarding these organs from external forces and potential injuries.
Respiratory Function

The trunk, particularly the abdominal muscles, plays a significant role in respiratory function. When we breathe, the diaphragm and abdominal muscles contract and relax, creating a negative pressure that draws air into the lungs. This coordinated effort ensures efficient gas exchange and proper oxygenation of the body.
Common Issues and Injuries

Despite its strength and resilience, the trunk is susceptible to various issues and injuries. Some of the most common problems include:
- Back Pain: Back pain is a prevalent issue, affecting people of all ages and activity levels. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strains, herniated discs, poor posture, or underlying medical conditions.
- Spinal Injuries: Injuries to the spine, such as fractures or dislocations, can result from accidents, sports-related incidents, or falls. These injuries can have severe consequences and may require immediate medical attention.
- Abdominal Muscle Strains: Strains or tears in the abdominal muscles can occur due to overexertion, improper lifting techniques, or sudden movements. These injuries can be painful and may limit mobility.
- Rib Injuries: Rib injuries, such as fractures or bruising, often occur as a result of direct impact or trauma. They can be extremely painful and may restrict breathing and movement.
Maintaining Trunk Health

Taking care of your trunk is essential for overall well-being and mobility. Here are some tips to maintain the health and function of your trunk:
- Posture: Maintain good posture throughout the day. Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this can put unnecessary strain on your spine and muscles.
- Exercise: Incorporate core-strengthening exercises into your fitness routine. These exercises, such as planks, bridges, and deadlifts, help strengthen the muscles of the trunk, improving stability and balance.
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle strains. Focus on stretching the back, abdominal, and oblique muscles to maintain optimal range of motion.
- Ergonomics: Pay attention to your work and living environment. Ensure your desk, chair, and computer setup promote good posture and reduce strain on your trunk.
- Lifting Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, use proper form and technique. Bend your knees, keep your back straight, and engage your core muscles to avoid injuries.
Conclusion

The trunk, often an unsung hero of the human body, plays a vital role in our daily lives. Its complex structure and functions enable us to move, breathe, and protect our vital organs. By understanding the importance of the trunk and taking care of its health, we can maintain optimal physical performance and well-being. So, the next time you bend, twist, or lift, remember the hard-working trunk that makes it all possible.
What are some common exercises to strengthen the trunk muscles?

+
There are numerous exercises that target the trunk muscles. Some popular options include planks, Russian twists, bird dogs, deadlifts, and various yoga poses such as the cobra and the cat-cow.
How can I improve my posture to reduce back pain?

+
Improving your posture can significantly reduce back pain. Focus on standing or sitting with your shoulders back and down, your chest lifted, and your core engaged. Avoid slouching or hunching over, and take breaks to stretch and move throughout the day.
Are there any specific stretches for the trunk muscles?

+
Yes, there are several stretches that target the trunk muscles. Some examples include the spine twist, the cat-cow stretch, the child’s pose, and the cobra pose. These stretches help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension in the trunk.
What are some common causes of back pain?
+Back pain can be caused by various factors, including muscle strains, herniated discs, poor posture, obesity, and underlying medical conditions such as arthritis or osteoporosis. It’s important to identify the specific cause of your back pain to determine the most effective treatment approach.
Can trunk injuries be prevented?
+While it’s not always possible to prevent injuries, taking certain precautions can significantly reduce the risk. This includes maintaining good posture, using proper lifting techniques, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the trunk muscles, and avoiding excessive strain or impact on the trunk.
