Section 404 Clean Water Act

The Clean Water Act (CWA) is a landmark legislation in the United States that aims to protect and restore the integrity of the nation's water bodies, ensuring clean and safe water for all. Section 404 of the CWA plays a crucial role in regulating the discharge of dredged or fill material into waters of the United States, including wetlands. This section empowers the Army Corps of Engineers and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to manage and control activities that may impact these vital ecosystems.
Understanding Section 404
Section 404 of the Clean Water Act establishes a permit program to regulate the placement of dredged or fill material into navigable waters, including wetlands. It grants authority to the Secretary of the Army, acting through the Chief of Engineers, to issue permits, ensuring that any discharge of these materials does not cause significant degradation to the nation's waters.
The EPA also plays a significant role in the implementation of Section 404 by providing guidelines and setting water quality standards. This collaborative effort between the Army Corps of Engineers and the EPA ensures a comprehensive approach to protecting the environment.
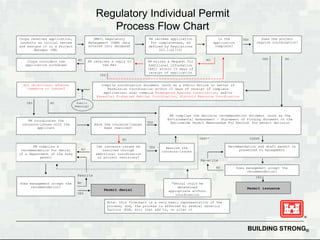
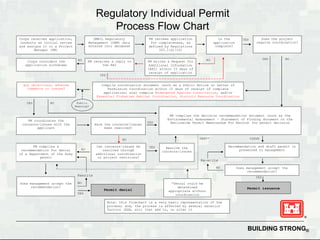
The Permit Process

Obtaining a Section 404 permit involves a thorough evaluation process. Here's a simplified breakdown of the steps involved:
- Pre-Application Consultation: Before submitting a formal application, it is recommended to consult with the Army Corps of Engineers to discuss the proposed project and potential impacts on water resources.
- Application Submission: Prepare and submit a detailed application, including project plans, environmental assessments, and any necessary supporting documentation.
- Review and Evaluation: The Army Corps of Engineers conducts a thorough review, considering the project's potential impacts on water quality, aquatic ecosystems, and any potential alternatives.
- Public Notice and Comment Period: To ensure transparency, a public notice is issued, inviting interested parties to provide comments and feedback on the proposed project.
- Decision and Permit Issuance: Based on the review and public comments, the Army Corps of Engineers makes a decision. If approved, a permit is issued with specific conditions and requirements to minimize environmental impacts.
It's important to note that the permit process may vary depending on the complexity of the project and the specific water bodies involved. The Army Corps of Engineers and the EPA work together to ensure a balanced approach, considering both economic development and environmental protection.
Environmental Impact Assessments

A key aspect of the Section 404 permit process is the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). This assessment evaluates the potential effects of a proposed project on the environment, including water quality, habitat loss, and the overall ecological balance. The EIA helps identify mitigation measures and alternative solutions to minimize adverse impacts.
The EIA process involves extensive data collection, field surveys, and modeling to understand the project's potential environmental consequences. It provides a scientific basis for decision-making and ensures that any approved projects have a minimal negative impact on the environment.
Wetland Protection and Restoration
Section 404 of the Clean Water Act places a strong emphasis on wetland protection and restoration. Wetlands are vital ecosystems that provide numerous benefits, such as flood control, water filtration, and habitat for diverse plant and animal species.
The permit program under Section 404 aims to minimize the loss of wetlands and promote their restoration and enhancement. It requires applicants to demonstrate that their projects avoid and minimize impacts on wetlands, and in cases where impacts are unavoidable, to provide compensatory mitigation to offset any losses.
Compensatory Mitigation

Compensatory mitigation is a crucial component of the Section 404 permit process. It involves creating, restoring, enhancing, or preserving wetlands or other aquatic resources to offset the unavoidable impacts of a project. The goal is to ensure that any losses in wetland functions and values are fully compensated for.
There are different approaches to compensatory mitigation, including on-site mitigation, where the project proponent creates or restores wetlands on their own property, and off-site mitigation, where mitigation occurs at an approved wetland mitigation bank or through an in-lieu fee program.
Enforcement and Compliance

The Army Corps of Engineers and the EPA have established robust enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance with Section 404 permits. Non-compliance can result in penalties, including civil and criminal penalties, as well as the requirement to cease activities and restore the impacted area.
Regular inspections and monitoring are conducted to verify compliance with permit conditions. Additionally, the public plays a vital role in reporting any suspected violations, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the enforcement process.
Collaboration and Public Involvement

The implementation of Section 404 of the Clean Water Act relies on collaboration between government agencies, project proponents, and the public. Public involvement is encouraged throughout the permit process, allowing for input and feedback on proposed projects.
Public hearings, meetings, and comment periods provide opportunities for stakeholders to express their concerns, share scientific data, and propose alternative solutions. This collaborative approach ensures that the final decisions consider the interests and values of the community.
Challenges and Controversies

While Section 404 of the Clean Water Act has made significant strides in protecting water resources, it has also faced challenges and controversies. Some critics argue that the permit process can be complex and time-consuming, potentially hindering economic development projects.
There have been instances where the interpretation and implementation of Section 404 have been disputed, leading to legal challenges. Additionally, the effectiveness of compensatory mitigation and the long-term success of wetland restoration efforts have been subjects of debate among environmental experts.
The Future of Water Protection

As the world faces increasing environmental challenges, the role of Section 404 of the Clean Water Act becomes even more crucial. The ongoing efforts to protect and restore water bodies, including wetlands, are essential for maintaining the health of ecosystems and ensuring the availability of clean water for future generations.
The continuous refinement of the permit process, advancements in environmental science, and the integration of innovative technologies offer hope for more effective and sustainable water protection measures. By striking a balance between economic development and environmental conservation, we can work towards a greener and more resilient future.
🌊 Note: The information provided offers a concise overview of Section 404 of the Clean Water Act. For detailed guidance and specific requirements, it is essential to refer to the official regulations and guidelines published by the Army Corps of Engineers and the Environmental Protection Agency.
What is the primary purpose of Section 404 of the Clean Water Act?

+
Section 404 aims to regulate the discharge of dredged or fill material into waters of the United States, including wetlands, to prevent significant degradation of water quality and protect vital ecosystems.
Who is responsible for issuing Section 404 permits?

+
The Secretary of the Army, acting through the Chief of Engineers, is responsible for issuing Section 404 permits, with guidance and oversight from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
What is the role of Environmental Impact Assessments in the permit process?

+
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) evaluate the potential environmental impacts of a proposed project, providing scientific data to inform decision-making and ensure that any approved projects have minimal negative effects on the environment.
How does Section 404 contribute to wetland protection and restoration?

+
Section 404 emphasizes the protection and restoration of wetlands by requiring applicants to avoid and minimize impacts on these vital ecosystems and providing mechanisms for compensatory mitigation to offset any unavoidable losses.


