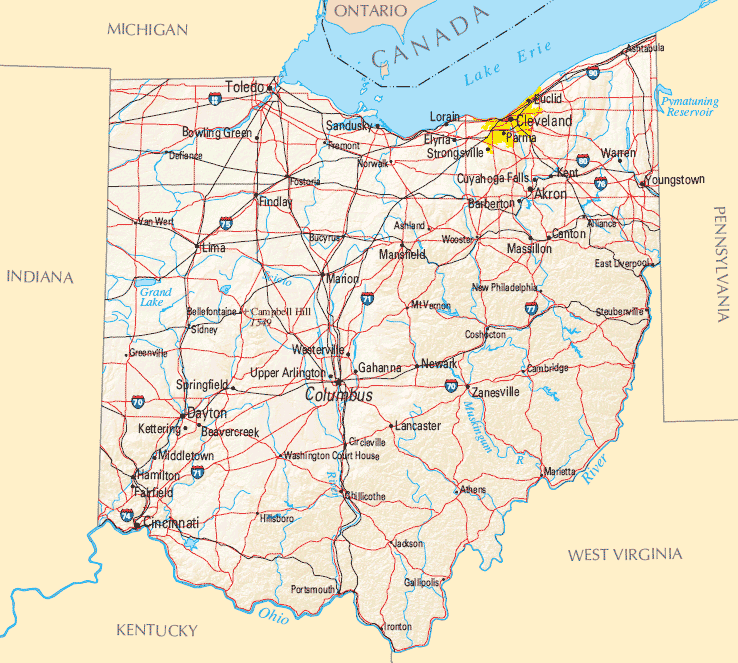
Design Ohio City Maps: The Ultimate Guide
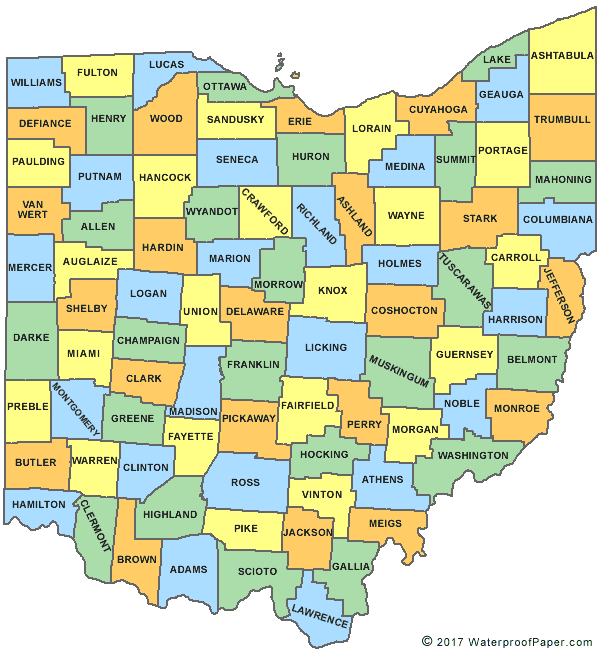
Welcome to the ultimate guide on designing Ohio City maps! Whether you're a cartographer, a city planner, or simply a geography enthusiast, this comprehensive tutorial will walk you through the process of creating detailed and visually appealing maps of Ohio's vibrant cities. From gathering data to finalizing your masterpiece, we'll cover every step to ensure your map becomes a valuable resource for both locals and visitors alike.
Understanding the Basics

Before diving into the intricacies of map design, it's essential to grasp the fundamental concepts that underpin the process. Here's a brief overview of some key terms and principles:
- Cartography: The art and science of mapmaking, encompassing the skills and techniques required to create accurate and informative maps.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Powerful tools that enable the collection, storage, analysis, and visualization of geographic data, forming the backbone of modern mapmaking.
- Map Projections: Methods used to represent the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map, each with its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the intended use.
- Map Scale: The ratio between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground, determining the level of detail and coverage of the map.
- Symbology: The use of symbols, colors, and patterns to represent geographic features and information on a map, ensuring clarity and consistency.
By familiarizing yourself with these concepts, you'll lay a solid foundation for your map design journey. Now, let's delve into the practical steps to create Ohio City maps that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Step 1: Define Your Purpose and Audience
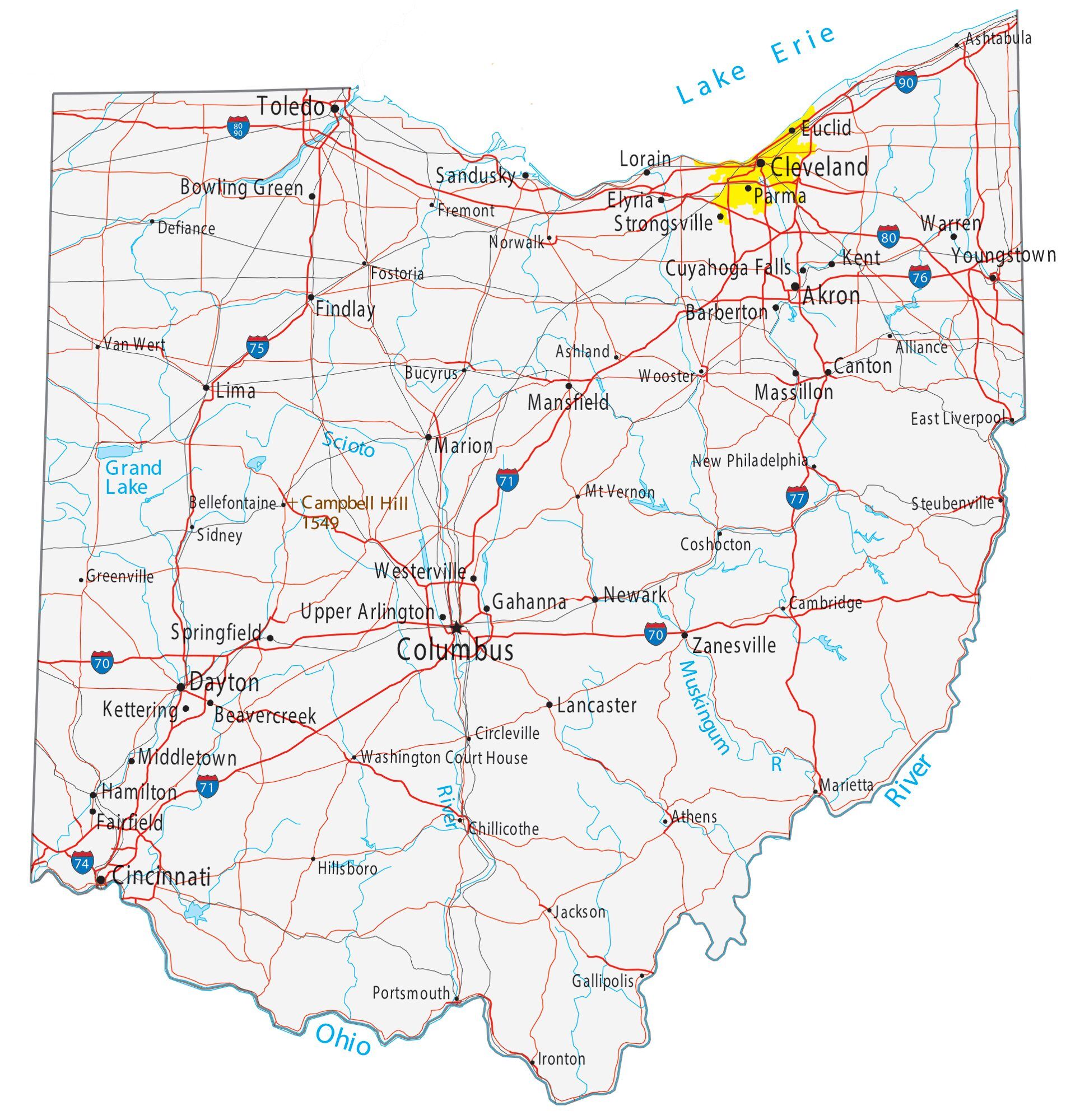
The first step in designing an effective map is to clearly define its purpose and target audience. Consider the following questions:
- What is the primary goal of your map? Is it to provide navigation assistance, showcase demographic data, or highlight cultural attractions?
- Who will be using your map? Tourists, locals, businesses, or government agencies? Understanding your audience's needs and expectations is crucial for making informed design choices.
For instance, if your map is intended for tourists, you might prioritize the inclusion of landmarks, tourist attractions, and public transportation routes. On the other hand, a map designed for local residents might emphasize neighborhood boundaries, parks, and community facilities.
Step 2: Gather Data and Resources

To create an accurate and comprehensive map, you'll need to gather relevant data and resources. Here are some key sources to consider:
- Government Agencies: Reach out to local government bodies, such as city planning departments or transportation authorities, for official data on streets, boundaries, and public infrastructure.
- OpenStreetMap (OSM): OSM is a collaborative project that provides free geographic data, offering a wealth of information on roads, buildings, and points of interest. You can contribute to and utilize this valuable resource for your map.
- Satellite Imagery: High-resolution satellite images can provide valuable context and detail for your map, especially when combined with other data sources.
- Local Businesses and Organizations: Engage with local businesses, community groups, and cultural institutions to gather information on attractions, events, and unique features specific to the city.
Remember to verify the accuracy and reliability of your data sources, as this will directly impact the quality of your final map.
Step 3: Choose Your Map Projection and Scale
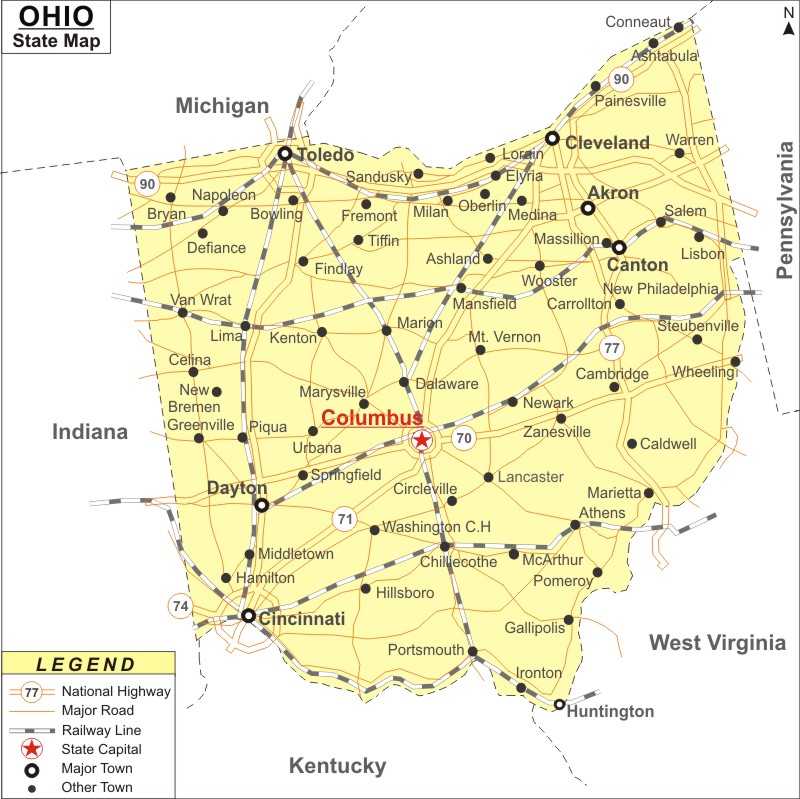
Map projections and scale are crucial decisions that will impact the appearance and usability of your map. Consider the following factors:
- Map Projection: Select a projection that minimizes distortion in the area of interest. For Ohio City maps, projections like the Albers Equal Area Conic or the Transverse Mercator might be suitable choices.
- Map Scale: Determine the appropriate scale based on the level of detail required. A larger scale (e.g., 1:10,000) will show more detail but cover a smaller area, while a smaller scale (e.g., 1:100,000) will provide a broader overview but with less detail.
Keep in mind that the choice of projection and scale will affect the visual appearance of your map, so it's essential to strike a balance between clarity and readability.
Step 4: Select Your Map Software
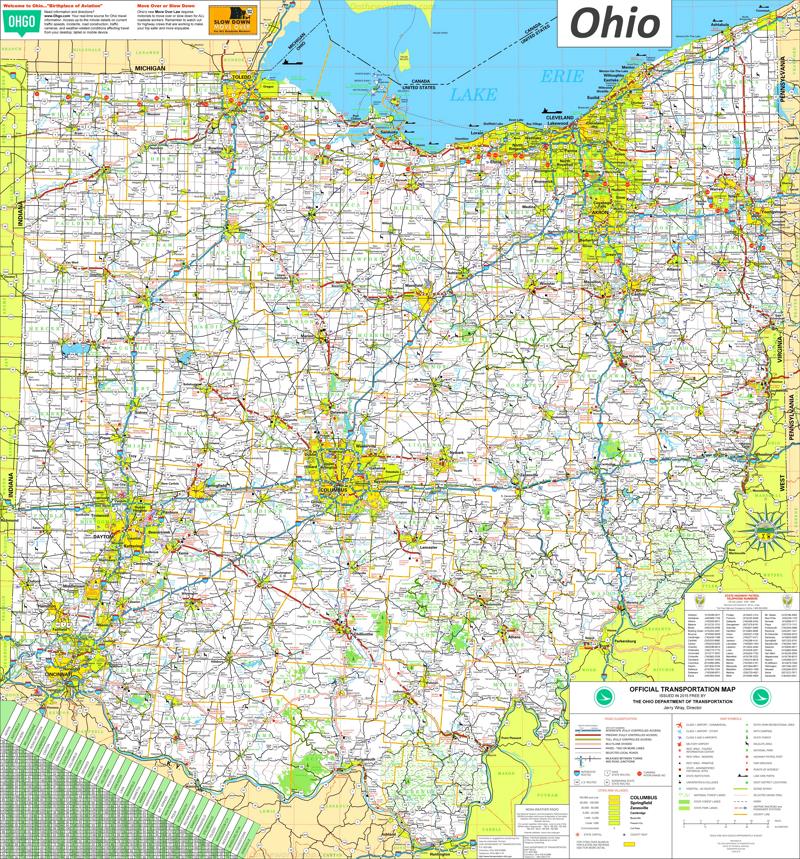
There are numerous software options available for map design, each with its own strengths and features. Here are some popular choices:
- QGIS: A powerful and open-source GIS software that offers a wide range of tools for map creation, data analysis, and visualization. QGIS is a popular choice for both beginners and professionals.
- ArcGIS: Developed by Esri, ArcGIS is a comprehensive suite of GIS software with advanced features for data management, analysis, and map production. It's widely used in professional mapping and spatial analysis.
- Adobe Illustrator: While primarily a vector graphics editor, Illustrator can be used for map design, offering precise control over shapes, colors, and text. It's particularly useful for creating visually appealing maps with custom designs.
Evaluate your needs, budget, and skill level to choose the software that best suits your requirements. Many of these tools offer free trials or open-source versions, allowing you to explore their capabilities before committing to a purchase.
Step 5: Design Your Map Layout
The layout of your map is crucial for organizing and presenting information effectively. Consider the following elements:
- Title and Legend: Choose a clear and descriptive title for your map, and create a legend that explains the symbols, colors, and patterns used. Ensure that the legend is easily accessible and understandable.
- Map Elements: Decide on the placement of essential map elements such as the north arrow, scale bar, and grid lines. These elements provide context and orientation for users.
- Labels and Text: Determine the font, size, and placement of labels for streets, landmarks, and other features. Clear and legible text is essential for an effective map.
- Color Scheme: Select a color palette that is visually appealing and enhances the readability of your map. Consider using contrasting colors for different features to ensure they stand out.
Experiment with different layouts and designs to find the one that best showcases the information you want to convey. Remember, a well-designed map layout can make your map more engaging and user-friendly.
Step 6: Add Base Layers and Features

Now it's time to start building your map by adding base layers and geographic features. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Base Layers: Begin by adding the base layers that form the foundation of your map. These could include terrain, roads, water bodies, and administrative boundaries.
- Point Features: Add points to represent specific locations, such as landmarks, attractions, or points of interest. Ensure that the symbols and labels are appropriately sized and placed.
- Line Features: Incorporate line features to represent roads, rivers, and other linear elements. Consider the thickness and style of the lines to ensure they are visually distinct.
- Polygon Features: Use polygon features to represent areas such as parks, neighborhoods, or administrative divisions. Choose appropriate colors and patterns to differentiate these areas.
- Text and Labels: Add text and labels to provide additional information about the features on your map. Ensure that the text is clear, well-spaced, and easy to read.
As you add these layers and features, pay attention to the overall balance and hierarchy of your map. Avoid overcrowding and ensure that the most important elements stand out.
Step 7: Refine and Enhance Your Map

Once you've added the essential layers and features, it's time to refine and enhance your map to make it truly exceptional. Here are some techniques to consider:
- Symbology and Visual Hierarchy: Experiment with different symbol styles, colors, and sizes to create a visual hierarchy that guides the user's eye and emphasizes important features.
- Incorporating Imagery: Add high-quality satellite or aerial imagery to provide a realistic and detailed backdrop for your map. This can add depth and context to your design.
- Thematic Mapping: Use color-coded maps to represent specific themes or data, such as population density, income levels, or environmental factors. Thematic maps can provide valuable insights and engage users.
- 3D Effects: Consider adding subtle 3D effects to your map to create a sense of depth and realism. This can be achieved through shading, elevation modeling, or the use of perspective views.
Remember to strike a balance between visual appeal and clarity. Your map should be aesthetically pleasing without sacrificing readability and usability.
Step 8: Quality Assurance and Testing
Before finalizing your map, it's crucial to conduct thorough quality assurance and testing. Here's what you should do:
- Accuracy Check: Verify the accuracy of your data and map elements. Double-check street names, boundaries, and feature locations to ensure they match the real-world conditions.
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability tests with a small group of users to gather feedback on the map's effectiveness and ease of use. Ask them to perform tasks and provide feedback on clarity, navigation, and overall user experience.
- Printing and Reproduction: If your map is intended for print, test different printing methods and paper types to ensure the final product meets your expectations. Consider factors such as color accuracy and resolution.
By conducting rigorous quality assurance and testing, you can identify and address any issues before releasing your map to the public.
Step 9: Share and Distribute Your Map

Once your map is complete and has passed quality assurance, it's time to share it with the world! Here are some distribution channels to consider:
- Online Map Portals: Upload your map to online platforms such as Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, or Mapbox, making it accessible to a global audience.
- Printed Materials: Consider printing your map as a brochure, poster, or guide for distribution at tourist information centers, hotels, or local businesses.
- Digital Distribution: Create a digital version of your map that can be accessed through websites, mobile apps, or interactive kiosks. This allows users to zoom, pan, and interact with your map easily.
- Social Media and Marketing: Promote your map through social media platforms and local marketing channels. Share preview images, highlight unique features, and engage with your audience to generate interest.
By utilizing a combination of these distribution channels, you can ensure that your map reaches a wide audience and becomes a valuable resource for Ohio City visitors and residents alike.
Notes
🌟 Note: Always ensure you have the necessary permissions and licenses to use data and images in your map. Respect copyright laws and attribute sources where applicable.
🖌️ Note: Experiment with different design styles and color schemes to find the one that best suits your map's purpose and audience. Don't be afraid to be creative and make your map stand out!
📐 Note: When working with spatial data, precision is key. Double-check your measurements and coordinates to ensure the accuracy of your map.
🤝 Note: Collaborate with local experts, historians, and community members to gather unique insights and stories that can enhance the narrative of your map.
📢 Note: Engage with your audience and gather feedback to continuously improve and update your map. User feedback is invaluable for creating maps that truly meet their needs.
Conclusion
Designing Ohio City maps is a rewarding endeavor that combines creativity, technical skills, and a deep appreciation for geography. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create visually stunning and informative maps that capture the essence of Ohio's vibrant cities. Remember to define your purpose, gather reliable data, choose the right tools, and pay attention to detail throughout the design process. With your map in hand, both locals and visitors will have a valuable resource to navigate and explore the wonders of Ohio.
FAQ
How can I ensure the accuracy of my map data?

+
To ensure accuracy, cross-reference your data with multiple sources, such as government records, satellite imagery, and local knowledge. Regularly update your data to reflect any changes in the real world.
What are some common challenges in map design and how can I overcome them?

+
Common challenges include data availability, map projection distortion, and visual clutter. To overcome these, carefully select your data sources, choose an appropriate map projection, and focus on creating a clear and balanced layout.
How can I make my map interactive and engaging for users?
+
Incorporate interactive elements such as pop-up boxes with additional information, tooltips, and zoom functionality. Add layers that users can toggle on and off to explore different themes or data sets.
What are some best practices for map labeling and typography?

+
Use clear and legible fonts, avoid overcrowding labels, and consider the hierarchy of information. Place labels strategically to avoid overlap and ensure they are easily readable at different zoom levels.
How can I ensure my map is accessible to people with visual impairments?

+
Incorporate accessibility features such as alt text for images, color contrast guidelines, and keyboard navigation. Consider providing a text-based version of your map or adding audio descriptions for key features.

